Land-Atmosphere Interactions
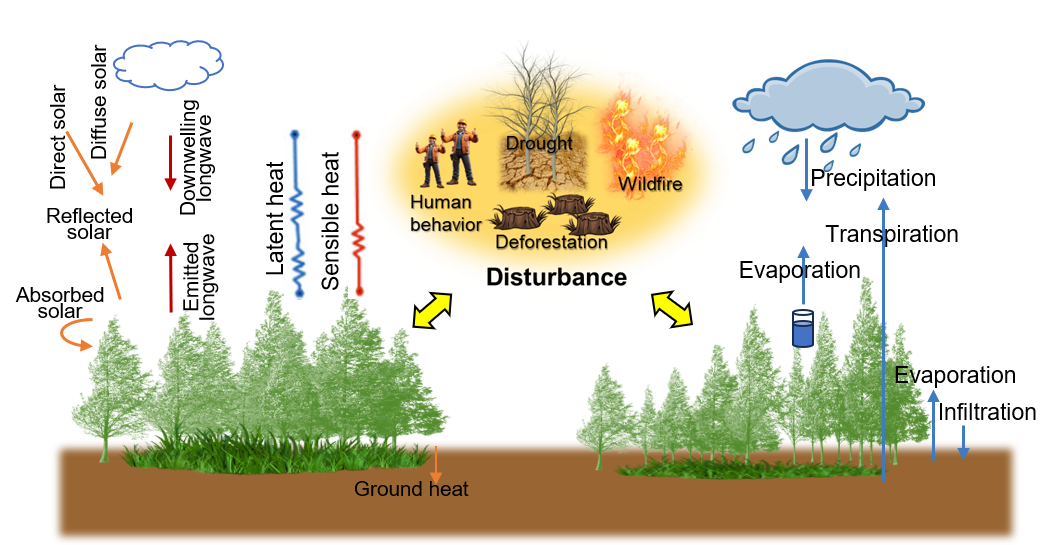
We study biophysical processes in water and energy cycles that affect temperature and water availability, and how they change under disturbances (e.g., deforestation, land cover change).
Global land dissipates approximately 12-35% and 50-58% of its absorbed solar radiation into sensible heat and latent heat fluxes, respectively. These fluxes play critical roles in regulating surface and atmospheric temperatures, as well as water availability, thereby influencing climate dynamics and ecosystem health. A better understanding of biogeophysical processes affecting ecosystem energy-water-carbon nexus is essential for enhancing earth system projections and guiding effective nature-based solutions. We investigate how abiotic and biotic factors, and disturbances (e.g., land-use and land-cover change, deforestation, drought, wildfire) reshape land surface energy partitioning and ecosystem functioning using causal inference, machine learning, Earth system models, and field measurements.
Related publications:
2024
- Global impacts of vegetation clumping on regulating land surface heat fluxesAgricultural and Forest Meteorology, 2024
2023
- Vegetation clumping modulates global photosynthesis through adjusting canopy light environmentGlobal Change Biology, 2023
2022
- Understanding and reducing the uncertainties of land surface energy flux partitioning within CMIP6 land modelsAgricultural and Forest Meteorology, 2022
2021
- Deforestation reshapes land-surface energy-flux partitioningEnvironmental Research Letters, 2021